Hive QL多表连接查询
Hive中的join概念和RDBMS中是一样的。到目前为止,Hive只支持基于等值条件的join连接,Hive并不支持任何基于非等值条件的join连接。
HiveQL多表连接查询的语法如下:
join_table:
table_reference [INNER] JOIN table_factor [join_condition]
| table_reference {LEFT|RIGHT|FULL} [OUTER] JOIN table_reference join_condition
| table_reference LEFT SEMI JOIN table_reference join_condition
| table_reference CROSS JOIN table_reference [join_condition] (as of Hive 0.10)
table_reference:
table_factor
| join_table
table_factor:
tbl_name [alias]
| table_subquery alias
| ( table_references )
join_condition:
ON expression
1、Hive支持表间的等值连接,能够联合两张表的数据。
语法:
SELECT table_fields
FROM table_one
JOIN table_two
ON (table_one.key_one = table_two.key_one
AND table_one.key_two = table_two.key_two);
2、Hive支持内连接、左外连接、右外连接和全外连接。Hive只支持等值连接,连接谓词中不支持or。
语法:
SELECT table_fields
FROM table_one
JOIN table_two
[LEFT, RIGHT, FULL OUTER] JOIN table_two
ON (table_one.key_one = table_two.key_one AND table_one.key_two = table_two.key_two);
使用左外连接、右外连接和全外连接
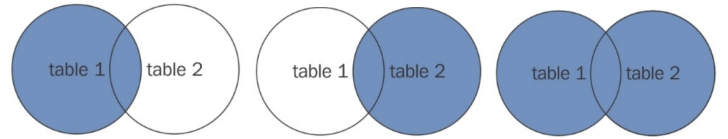
例如:
select * from Sales a LEFT OUTER JOIN Sales_orc b ON a.id = b.id; select * from Sales a RIGHT OUTER JOIN Sales_orc b ON a.id = b.id; select * from Sales a FULL OUTER JOIN Sales_orc b ON a.id = b.id; select * from Sales a LEFT OUTER JOIN Sales_orc b ON a.id = b.id WHERE a.fname = 'John'; select * from Sales a RIGHT OUTER JOIN Sales_orc b ON a.id = b.id WHERE a.fname = 'John';
3、使用左半连接(Left Semi-Joins)
左半连接用来查看左表中符合JOIN条件的记录。左半连接被用来在Hive中替代IN/EXISTS子查询。Hive可以使用semi join命令来处理这样的查询。在左半连接中,右手边的表只可以被用在join子句中,不可以用在where子句或select子句中。 其语法如下:
SELECT table_fields
FROM table_one
LEFT SEMI JOIN table_two
ON (table_one.key_one = table_two.key_one);
例如:
SELECT a.* FROM Sales a LEFT SEMI JOIN Sales_orc b ON a.id = b.id;
下面两句执行时会出错:
SELECT a.*, b.* FROM Sales a LEFT SEMI JOIN Sales_orc b ON a.id = b.id; SELECT a.* FROM Sales a LEFT SEMI JOIN Sales_orc b ON a.id = b.id WHERE b.id = 1;
4、交叉连接(cross join)
即笛卡尔集连接。在进行表连接时,cross join不是一个高效地、优化的方式。
例如:
SELECT * FROM Sales JOIN Sales_orc; SELECT * FROM Sales JOIN Sales_orc WHERE Sales.id = 1; SELECT * FROM Sales CROSS JOIN Sales_orc; SELECT * FROM Sales a CROSS JOIN Sales_orc b JOIN Location c on a.id = c.id;
5、使用带单个MapReduce的连接
如果相同的key被用在一个连接链中的话,Hive支持使用单个MapReduce在多个表间连接。
例如,要执行一个三表连接,其语法如下:
SELECT table_one.key_one, table_two.key_one, table_three.key_one
FROM table_one
JOIN table_two
ON (table_one.key_one = table_two.key_one)
JOIN table_three
ON (table_three.key_one = table_two.key_one);
6、使用最大表最后(Largest Table Last)
Hive执行join的方式:缓冲第一张表,然后将最后一张表映射到它们。最佳实践:总是最后列出最大的表,因为这将加快处理速度。
语法:
SELECT table_one.key_one, table_two.key_one, table_three.key_one
FROM table_one
JOIN table_two ON (table_one.key_one = table_two.key_one)
JOIN table_three ON (table_three.key_one = table_two.key_one);
其中table_one和table_two缓存在内存,而table_three直接从磁盘映射。
7、map端join
当在Hive中进行多表连接时,会有这样的场景:其中一个表较小(行较少),而另一个表较大。为了以更有效的方式得到结果,Hive使用map-side join。
在map-side join中,将较小的表缓存在内存中,而大表通过mapper进行传输。 通过这样做,Hive只在mapper的一侧完成连接,从而消除了reducer job。通过这样做,性能得到了极大的提高。
在Hive中,使用map-side join的方式有两种:
- 在select关键字后使用/*+ MAPJOIN(<table_name>)*/ 暗示. 其中table_name必须是小表的表名。(这是旧的用法)
- 另一种方式是设置如下的属性为true,然后运行一个join查询:set hive.auto.convert.join=true;
select /*+ mapjoin(Sales_orc)*/ a.fname, b.lname from Sales a join Sales_orc b on a.id = b.id; select a.* from Sales a join Sales_orc b on a.id = b.id and a.fname = b.fname;
使用map端join有一些限制。下面是不支持使用map-side join:
- Union后跟MapJoin
- Lateral view后跟一个MapJoin
- Reduce sink (group by/join/sort by/cluster by/distribute by)后跟MapJoin
- MapJoin后跟union
- MapJoin后跟join
- MapJoin后跟MapJoin
注意:
/*+ MAPJOIN(table_name) */暗示应该只用于数据被排序过或表被分桶时。 在这种场景下,join自动地被转换到一个bucket map join或一个bucket sort merge map join, 所以,使用set hive.auto.convert.join=true; 来代替语句中的暗示。
Hive QL多表连接应用示例
1、使用相等连接来join连接表。
Hive支持表间的等值连接,能够让我们联合两张表的数据。
语法:
SELECT table_fields
FROM table_one
JOIN table_two
ON (table_one.key_one = table_two.key_one
AND table_one.key_two = table_two.key_two);
下面我们创建两个表,person和address表,填充数据,并对这两张表执行join连接操作。
-- 创建person表
create table if not exists person (
persid int,
pername string
)
clustered by (persid) into 1 buckets
stored as orc
tblproperties('transactional'='true');
-- 填充一些测试数据
insert into table person values
(0,'黄渤'),
(1,'黄晓明'),
(2,'迪丽热巴'),
(3,'岳云鹏');
-- 查询
select * from person;
-- 创建另一张表address
create table if not exists address(
persid int,
addr string
)
clustered by (persid) into 1 buckets
stored as orc
tblproperties('transactional'='true');
-- 填充一些数据
insert into table address values
(0,'北京'),
(1,'上海'),
(2,'乌鲁木齐');
-- 查询
select * from address;
-- 现在有了两张表,接下来执行join操作:
select person.pername, address.addr
from person join address on (person.persid = address.persid);
2、使用外连接
Hive支持表间的相等连接,使用left,right 和full outer连接。
语法:
SELECT table_fields
FROM table_one
LEFT, RIGHT, FULL OUTER] JOIN table_two
ON (table_one.key_one = table_two.key_one
AND table_one.key_two = table_two.key_two);
下面对person表和address表执行外连接操作。
-- 左外连接 select person.pername,address.addr from person left join address on (person.persid = address.persid); -- 右外连接 select person.pername,address.addr from person right join address ON (person.persid = address.persid); -- 全外连接 select person.pername,address.addr from person full outer join address (person.persid = address.persid);
3、使用左半连接(Left Semi-Joins)
select person.pername from person left semi join address on(person.persid = address.persid);
4、使用带单个MapReduce的连接
Hive支持使用单个MapReduce在多个表间连接,如果相同的key被用在一个连接链中的话。
语法:
SELECT table_one.key_one, table_two.key_one, table_three.key_one
FROM table_one
JOIN table_two
ON (table_one.key_one = table_two.key_one)
JOIN table_three
ON (table_three.key_one = table_two.key_one);
下面演示在一个MapReduce中实现三表连接。
-- 首先,创建第三张表account
create table account (
persid int,
bamount int
)
clustered by (persid) into 1 buckets
stored as orc
tblproperties('transactional'='true');
-- 填充一些数据
insert into table account values(1,12000),(2,9000);
-- 查询
select * from account;
-- 执行三表连接,以相同的列名作为连接列
select person.pername,address.addr,account.bamount
from person
join address on (person.persid = address.persid)
join account on (person.persid = account.persid);
注意底层的MapReduce job作业,会发现这个三表连接只需要一个MapReduce作业。
